Layer-1 blockchains are foundational networks supporting numerous functions immediately on their protocol, whereas Layer-2 blockchains function atop these foundational layers, enhancing scalability and effectivity. Evaluating the utilization and effectivity of EVM-compatible L1 and L2 blockchains and aspect chains helps us higher perceive the market values and the place a lot of the DeFi exercise comes from.
Dune Analytics knowledge analyzed by CryptoSlate confirmed Polygon, a Layer-2 sidechain, was the main determine within the DeFi ecosystem, carefully adopted by BNB Chain, an EVM-compatible Layer-1 blockchain.
One of the crucial necessary metrics when analyzing L1s and L2s is the day by day fuel utilization—the computational effort required to execute operations on the blockchain. Fuel charges are paid in native blockchain currencies, and excessive fuel utilization sometimes signifies strong community exercise. Notably, when L2 options preserve excessive fuel utilization at low USD prices, it displays an environment friendly scaling answer that makes transactions inexpensive with out sacrificing blockchain exercise.
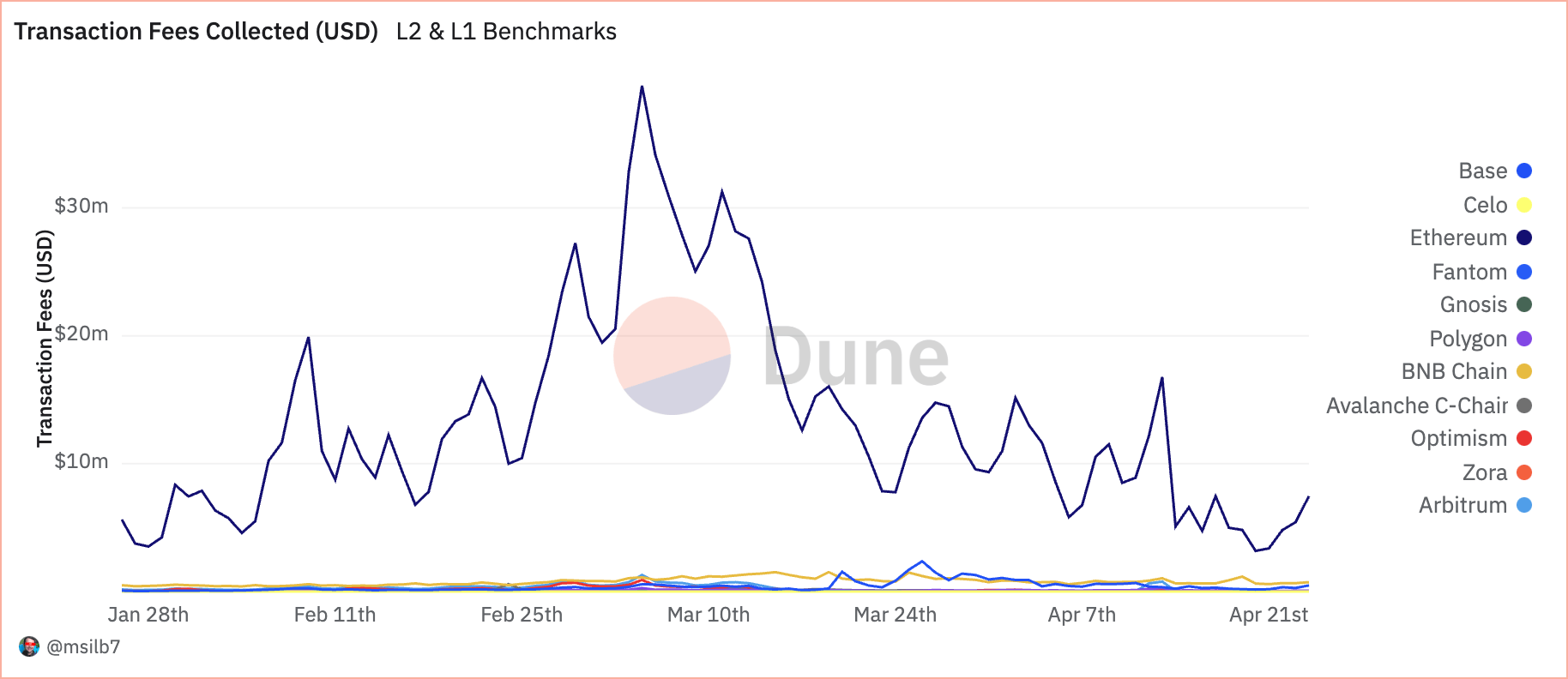
Polygon makes use of a mean of 579.97 billion models of native fuel day by day, with related prices amounting to only $65.48k. This interprets to a meager common of $0.76 in USD per second regardless of processing a excessive quantity of 48.37 transactions per second. Every transaction on Polygon prices about 138,782 fuel models. BNB Mainnet, whereas additionally excessive in transaction quantity, exhibits a unique value construction with 454.89 billion models of native fuel used day by day and $1.02 million in day by day USD charges; the associated fee per second soars to $11.81, far surpassing Polygon’s. The upper value per transaction, which averages 108,513 fuel models, displays BNB’s heavier computational demand per transaction, suggesting a extra resource-intensive operation than Polygon.
ChainAvg Native Fuel Used / DayAvg USD Fuel Charges / DayAvg # Txs / DayAvg Native Fuel per TxAvg Native Fuel Used / SecondAvg USD Fuel Charges / SecondAvg # Txs / SecondPolygon Mainnet579.97b$65.48k4.18m138,7826.71m$0.7648.37BNB Mainnet454.89b$1.02m4.06m108,5135.26m$11.8147.03Arbitrum One273.96b$250.05k1.14m241,2073.17m$2.8913.15Base Mainnet222.37b$378.72k1.26m174,2292.57m$4.3814.59OP Mainnet213.30b$160.26k490.83k429,1292.47m$1.855.68Gnosis Mainnet109.77b$1.05k182.58k601,2441.27m$0.012.11Ethereum Mainnet108.14b$12.63m1.19m90,7581.25m$146.2013.79Fantom Mainnet94.86b$4.89k248.93k372,5211.10m$0.062.88
Arbitrum makes use of 273.96 billion models of fuel day by day, costing customers $250.05k, which breaks right down to $2.89 per second and 241,207 fuel models per transaction, indicating a better value effectivity than BNB however much less so than Polygon. Base Mainnet data comparable developments with 222.37 billion models and day by day charges of $378.72k, leading to a barely larger per-second value of $4.38 and 174,229 models per transaction.
Ethereum operates with the best value affect, utilizing 108.14 billion fuel models day by day, translating right into a hefty $12.63 million in charges. With prices skyrocketing to $146.20 per second, regardless of having a mean of 90,758 fuel models per transaction, it illustrates Ethereum’s strong safety and computational breadth and highlights its scalability challenges that L2 networks purpose to deal with.
Taking a look at transaction metrics, knowledge from April 23 exhibits that Polygon led with 4.02 million transactions, adopted by BNB Chain with 3.9 million. These figures present robust person engagement and community utility, representing a respective 25.8% and 25.1% share of whole transactions (excluding recognized system transactions).
Nonetheless, when analyzing transaction charges, a unique narrative emerges. Regardless of a decrease transaction rely, Ethereum amassed $7.46 million in charges, representing a staggering 83.9% of whole charges collected. This discrepancy means that whereas Ethereum processes fewer transactions, its larger transaction prices replicate its major layer standing and the intensive computational assets required for operations.
In the case of DeFi apps, Polygon once more leads the transaction numbers, with 3.3 million app transactions, exhibiting it’s a go-to platform for DeFi actions.
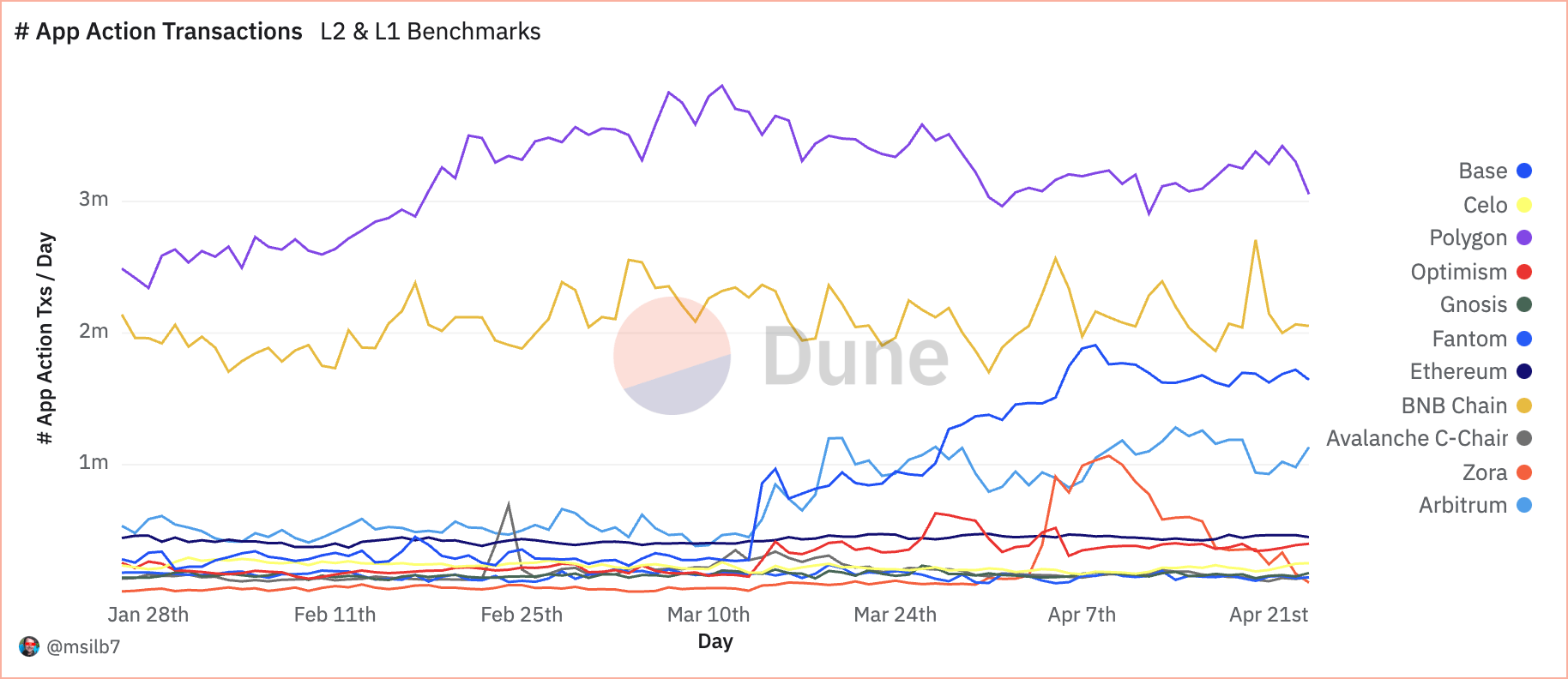
BNB Chain noticed 1.22 million transacting addresses, with Polygon barely behind at 1.18 million. These figures, contrasted with Ethereum’s 402.77k, recommend that different EVM-compatible networks have gotten most popular platforms for normal DeFi customers attributable to their decrease value buildings.
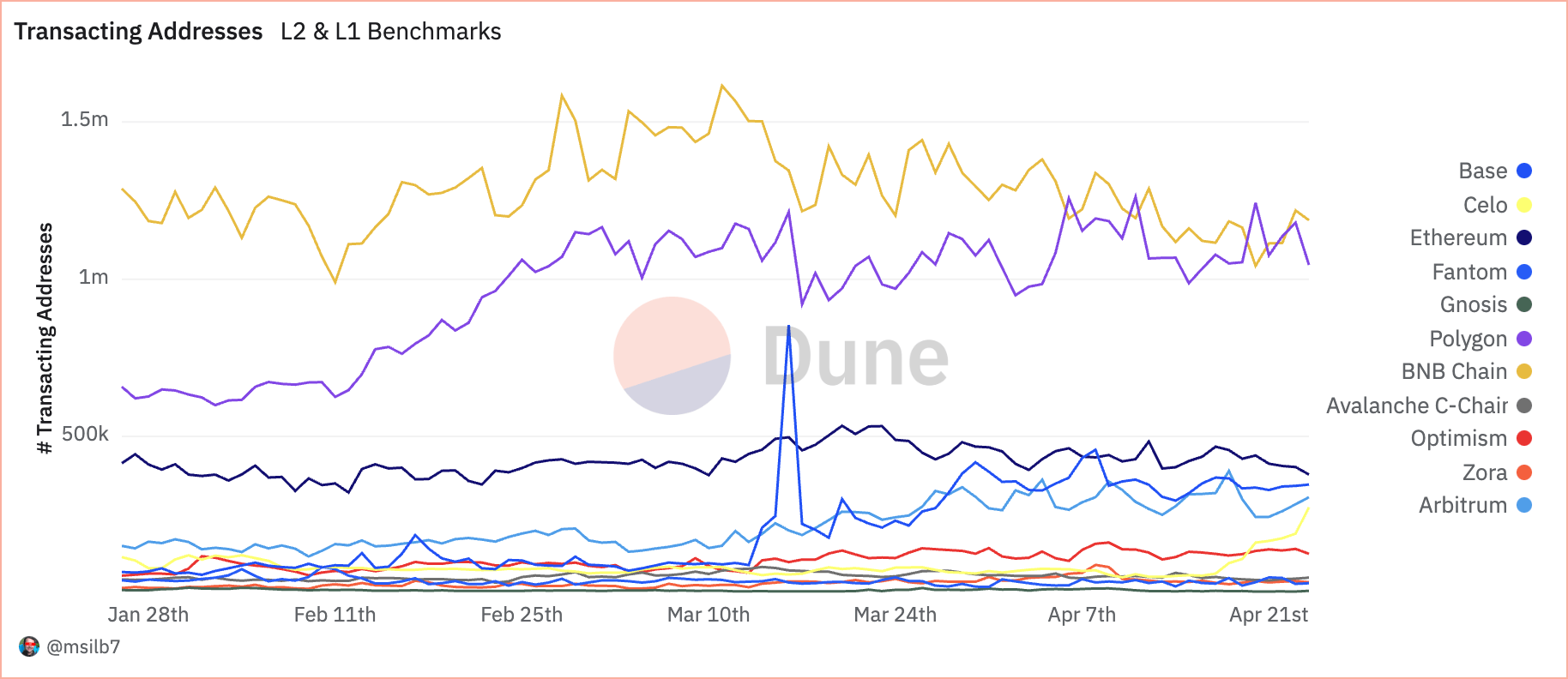
Analyzing the efficiency of those blockchains side-by-side exhibits a battle between foundational safety and enhanced scalability. Whereas L1 blockchains like Ethereum proceed to safe high-value transactions with substantial charges, scaling options like Polygon seize the majority of day by day transactions and software interactions, signifying a shift in direction of extra environment friendly and user-friendly blockchain infrastructures in DeFi.
It’s necessary to notice that regardless of being labeled as a Layer-2 blockchain by many, Polygon operates as an L2 sidechain for Ethereum, because it depends by itself set of validators and doesn’t rely upon Ethereum for safety. This permits Polygon to help extra experimental exercise than “true” L2 blockchains with out impacting Ethereum. One other truth price mentioning is that BNB Chain is an EVM-compatible Layer-1 blockchain however has positioned itself available on the market not as a competitor to Ethereum, one other L1, however to different L2s.
⛓️ High Layer 2 Crypto Property
View AllMentioned on this article