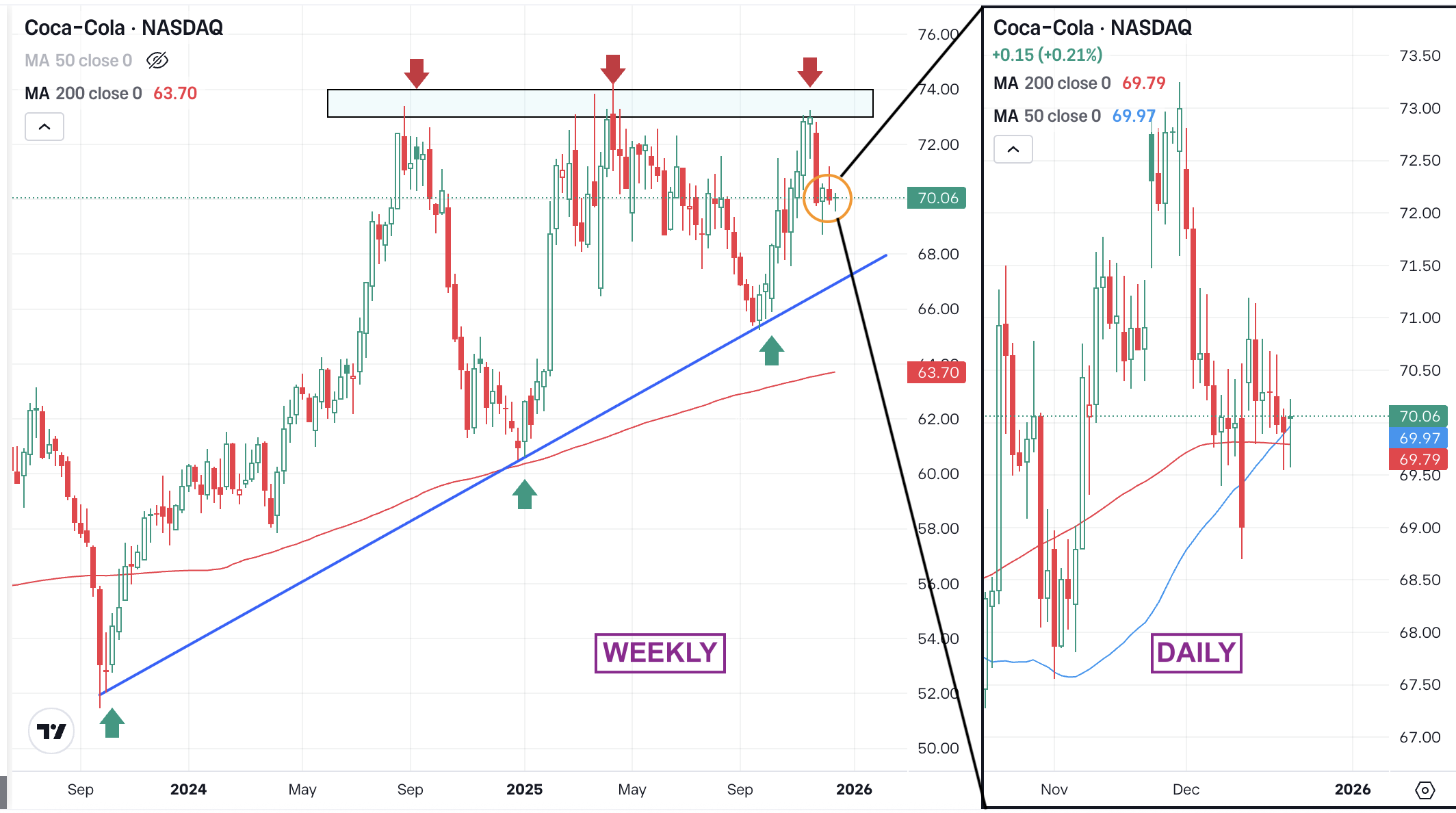
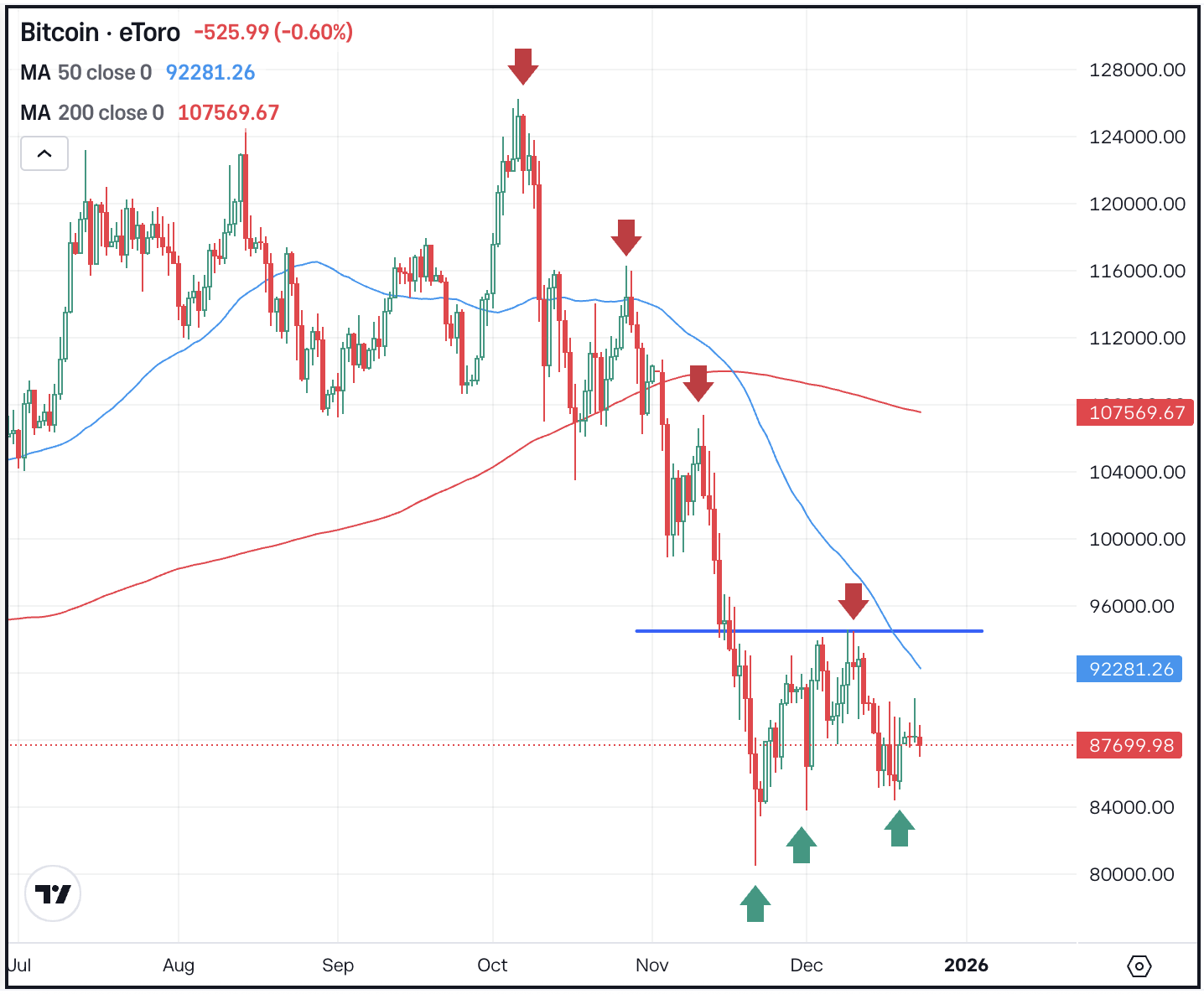
Belief Pockets’s Chrome extension shipped a malicious replace in December, exfiltrating pockets information and draining roughly $7 million from lots of of accounts earlier than the corporate pushed a repair.
The compromised model 2.68 was stay for days, auto-updating within the background, the way in which browser extensions are designed to. Customers who adopted each normal self-custody rule, reminiscent of by no means sharing their seed phrase, checking URLs, and utilizing respected wallets, nonetheless misplaced funds.
The assault focused the browser layer, not the blockchain, and it uncovered a persistent trade-off that the trade has spent years making an attempt to disregard: browser-extension wallets are always-on sizzling wallets sitting in probably the most hostile environments in computing.
This wasn’t an remoted case. MetaMask’s safety workforce documented a faux Google Chrome extension referred to as “Safery: Ethereum Pockets” that lived within the official Chrome Internet Retailer from late September till mid-November, stealing seed phrases.
Chainalysis estimates that crypto theft reached $3.4 billion in 2025, with private pockets compromises accounting for 20% of that complete, or $713 million. Nonetheless, that may have been 37% with out the Bybit change hack.
For perspective, private pockets compromises accounted for simply 7.3% of the stolen worth in 2022 and 44% in 2024, indicating that attackers are following the worth to wherever person keys stay.

The UX/safety trade-off that will not go away
Browser extensions sit in the identical setting as adware and random plugins. Campaigns like “ShadyPanda” and “GhostPoster” present how benign extensions will be up to date years later with code that steals cookies or executes distant instructions, by way of official replace channels.
The Belief Pockets case proves even respected wallets can briefly ship compromised updates, and customers settle for them as a result of extensions auto-update within the background. That is the trade-off: auto-updates patch vulnerabilities shortly but in addition ship dangerous code at scale.
Usability pushes customers towards blind signing as a result of ETH and EVM transactions are notoriously exhausting for normal customers to learn.
When approving swaps by way of a browser extension, most customers faucet “Affirm” on opaque hex blobs moderately than human-readable semantics.
In consequence, drainer kits exploit this by presenting transactions that look like routine approvals however grant full token-spending rights to attacker contracts.
The person technically approves each step, but has no thought what’s being signed. That is not a bug in person habits, however moderately a characteristic of how browser wallets reduce friction.

“Finest practices” nonetheless assume customers can reliably confirm context. For years, self-custody hygiene has meant: by no means share the seed, test URLs, use {hardware} wallets.
These stay obligatory however inadequate.
Pretend extensions by no means instantly ask for the seed phrase till the person “imports” a pockets. Conversely, they current acquainted UX, leaving customers to differentiate clones from the true factor.
The Chrome Internet Retailer vetting course of is meant to catch these, however it would not catch persistently.
For {hardware} pockets customers, the Ledger Join Equipment exploit from late 2023 illustrates the identical fault line. A former worker’s NPM account was phished, and attackers pushed a malicious package deal that injected draining code into any dApp utilizing the equipment.
Customers with Ledger {hardware} units nonetheless misplaced funds as a result of the browser-side integration was compromised. Even with the keys nonetheless on the gadget, customers signed draining transactions as a result of the browser’s logic had been tampered with.
Empirical information exhibits that fashions combining {hardware} key storage and air-gapped signing have incident charges beneath 5%, in contrast with over 15% for software-only wallets. Wallets with phishing detection and transaction alerts cut back user-reported losses by practically 60%.
Nonetheless, adoption is the catch: day-to-day DeFi exercise runs via browser extensions as a result of they’re the one setup most customers discover usable. The most secure configurations are too cumbersome, and the usable configurations are too uncovered.
The place the assaults truly occur
The weak hyperlinks in 2025 are virtually all “above” the chain, reminiscent of browser, extensions, and provide chain, whereas most person schooling nonetheless focuses on what occurs beneath, on the non-public key and seed storage degree.
The assault paths break down into 4 layers.

The browser and OS layer is the place info-stealer malware operates. Households like ModStealer, AmosStealer, and SantaStealer infect the machine, learn extension storage, intercept keystrokes, or hook browser APIs to seize seeds and personal keys at relaxation.
As TechRadar reported, these instruments are actually marketed on underground boards and Telegram as “stealer-as-a-service,” with modules devoted to grabbing browser credentials, cookies, and pockets information, then exfiltrating them in compressed chunks.
The browser is the entry level, and extensions are the payload.
The pockets extension layer is the place compromised or malicious updates function. Belief Pockets’s model 2.68, the faux “Safery” pockets, and the malicious wallets on Chrome all added code that exfiltrated secrets and techniques or tampered with transaction requests earlier than customers noticed them.
That is the UX and supply-chain trade-off in motion: auto-updates are essential for patching vulnerabilities, however additionally they ship dangerous code at scale when the replace mechanism itself is compromised.
The dApp and connector layer is the place libraries like Ledger Join Equipment get hijacked. When these are compromised upstream, official dApps begin presenting malicious transactions.
The person connects their actual pockets or {hardware} gadget, sees a normal-looking immediate, and indicators a drainer transaction. This layer is invisible to most customers, as they do not know which JavaScript libraries energy the dapps they use, they usually haven’t any strategy to confirm that these libraries have not been tampered with.
The RPC and blockchain layer is the place the assault completes. As soon as a malicious transaction is signed and broadcast, the remainder of the stack works as designed.
Funds transfer, and the one remaining defenses are monitoring, speedy incident response, and any off-chain restoration measures the ecosystem might need. By this level, the injury is finished. The blockchain did not fail, however the layers above it did.
What BTC and ETH holders ought to truly do
The guidelines for utilizing browser wallets hasn’t modified a lot in precept, however the emphasis must shift towards isolating the browser layer from the belongings that matter.
The desk beneath breaks down the important thing areas the place customers can cut back publicity with out abandoning browser wallets solely.
Decreasing pockets threat exposureAreaWhat to doWhy it mattersCold vs. sizzling storageKeep long-term BTC/ETH on {hardware} or multisig; use browser wallets just for working capital.Limits the injury if a browser extension or PC is compromised.Isolate your browserUse a devoted browser/profile for crypto with minimal extensions, put in from official hyperlinks.Shrinks the assault floor from shady add-ons and poisoned search adverts.Confirm extension and versionConfirm writer title and extension model in opposition to official pockets docs after main incidents.Catches faux or tampered extensions and compromised auto-updates.Seed phrase handlingNever kind your seed right into a browser or “assist” chat; when you did, migrate to a contemporary {hardware} pockets.Assumes any seed uncovered to the browser is burned and removes the lingering compromise.Approvals and permissionsRegularly overview and revoke token approvals; keep away from limitless allowances to obscure contracts.Reduces the blast radius of a single malicious dapp or drainer contract.Endpoint hygieneKeep OS and browser up to date; keep away from pirated software program; use respected AV tuned for info-stealers.Many trendy assaults come from malware that particularly hunts pockets extensions.Use pockets security featuresTurn on phishing safety, transaction simulation, and handle books the place out there.Provides machine checks on high of human judgment for suspicious domains and transactions.Add friction for large amountsFor massive transfers, require a second gadget, {hardware} pockets, or multisig approval path.Forces you out of the compromised browser path earlier than shifting life-changing sums.
The trade is aware of the issue and hasn’t mounted it
The Belief Pockets incident, the faux Chrome extensions, the Ledger Join Equipment exploit, and the rising share of non-public pockets compromises all level to the identical conclusion: the browser is a hostile setting, and “self-custody greatest practices” round seed phrases and {hardware} nonetheless do not totally handle that.
The failure mode has shifted from customers mishandling keys to attackers compromising the UX layer, and the trade has recognized this for years.
The structure hasn’t modified as a result of the alternate options are both too cumbersome for mass adoption or too centralized to suit the ethos.
Till browser wallets will be remoted from the broader browser setting, or till transaction signing occurs in a very air-gapped circulation that does not depend on JavaScript libraries and auto-updating extensions, the trade-off will persist.
Customers can observe each rule, use {hardware} wallets, by no means share their seeds, and nonetheless lose funds as a result of the code they’re interacting with, and which they haven’t any sensible strategy to audit, has been silently compromised.
That is not a user-education drawback. It is an structure drawback, and no quantity of “greatest practices” will repair it.